Describe the Role of the Following in Aerobic Cellular Respiration
This type of respiration is common in most of the plants and animals birds humans and other mammals. During aerobic cellular respiration glucose the main fountain of food energy is broken down in.
Cellular Respiration Review Article Khan Academy
The process by which mitochondria use to transfer the energy in foods to ATP is known as cellular respiration.
. Oxidative phosphorylation marks the terminal point of the cellular respiration and the main sequence that accounts for the high ATP yield of aerobic cellular respiration. Organisms such as prokaryotes and eukaryotes use respiration mechanisms for the breakdown of food that may require environmental oxygen. Where does the aerobic.
Cellular respiration whether aerobic or. Oxygen is an important part of. Cellular respiration has three steps each designed to generate NADH.
The protons flow back into the matrix through an enzyme called ATP synthase making ATP. Aerobic cellular respiration is a biological processes performed mainly by eukaryotic cells at the mitochondria. A Chemiosmosis is the movement of electrons down their electrochemical gradient which generates energy in the electron transport chain.
What is the role of NAD and fadh in aerobic respiration. Describe the role of oxygen in cellular respiration Cellular respiration is the process that produces energy in cells. Which of the following best describes the role of chemiosmosis in oxidative phosphorylation.
Description of the two coenzymes NAD and FAD and link them to each enzyme in glycolysis. These transfers are called redox reactions where the loss of electrons from one molecule oxidation must coincide with the addition of electrons to another substance reductionJul 11 2019. It is the process of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen gas to produce energy from food.
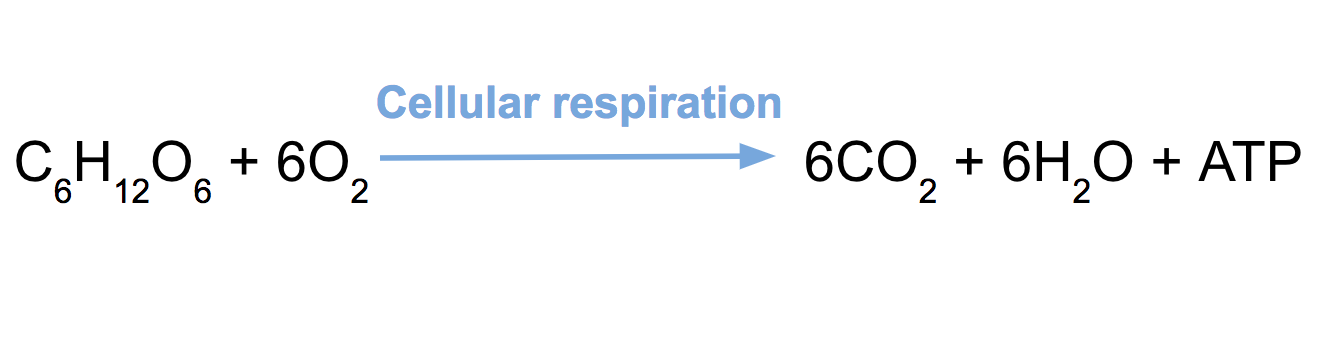
Carbon-based molecules from food and oxygen are used to make ATP. Aerobic cellular respiration has the chemical equation as follows. Accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain.
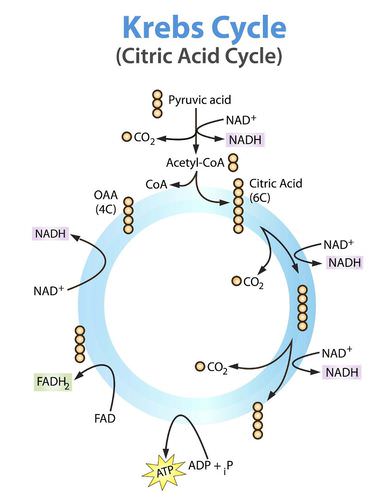
Describe redox reactions involved in the three steps of aerobic cellular respiration under the following topics. Acts as final electron acceptor of the ETC in aerobic respiration b. O combine to form pyruvic acid pyruvate are manufactured by the enzyme ATP synthase may be converted into acetyl CoA and enter the Krebs cycle when the body is in the post.
During cellular respiration a glucose molecule is gradually broken down into carbon dioxide and water. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NAD and flavin adenine dinucleotide FAD are two cofactors that are involved in cellular respiration. The correct description about cellular respiration is - option H.
Aerobic respiration provides energy to fuel all cellular processes. Basically aerobic cellular respiration is a process of energy conversion that releases energy from food in the presence of oxygen forming new compounds. The movement of hydrogens back into the matrix will provide the energy needed by ATP synthase to produce ATP.
A process of energy conversion that releases energy from food in the presence of oxygen forming new compounds The processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration both involve exchanges of two gasesoxygen and carbon dioxidewith the atmosphere. At the end of the electron transport chain oxygen accepts electrons and takes up protons to form water. For example ATP powers t the action of the sodium-potassium pump which allows us to move think and perceive the world around us.
B Chemiosmosis is the chemical breakdown of ATP into ADP and inorganic phosphate. Describe the role of NADH in aerobic respiration. During cellular respiration carbon skeletons are broken down and converted to other forms.
Describe the role of the following in aerobic cellular respiration. C Chemiosmosis is the movement of chemicals. In this process a food molecule breaks down in mitochondria may consume oxygen and transfer energy to cells in.
All cellular respiration uses glucose as a reactant and produces ATP. Name the three stages of aerobic respiration and state the cellular compartment or structure where each stage occurs. Acts as a catalytic enzyme d.
This compound is an essential component in intracellular energy transfer. ATP is then used as energy by nearly every cell in the body -- the largest user being the muscular system. Pyruvate oxidation and citric acid cycle using the backpack analogy that I described in class.
Aerobic respiration is a biological process that takes energy from glucose and other organic compounds to create a molecule called Adenosine TriPhosphate ATP. They are responsible for accepting high energy electrons and carrying them ultimately to the electron transport chain where they are used to synthesize ATP molecules. The reactions produce ATP which is then used to power other life-sustaining functions including growth repair and maintenance.
Explain the evolutionary significance of glycolysis. Oxygen is used as an electron acceptor within the electron transport chain of aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate or ATP. The main role of enzymes during the respiration reaction is to assist in transferring electrons from one molecule to another.
3 05 points Which of the following best describes the role of FADH and NADH in aerobic cellular respiration. Which of the following describes the fate of oxygen utilized directly during cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is the multistep metabolic process that takes place in the mitochondria of the cell.
Acts as energy carrying molecule c. In this process water and carbon dioxide are produced as end products. Although necessary for multicellular life in an ironic twist of fate aerobic cellular respiration is thought to also be responsible for the processes that end multicellular life.
It produces ATP and carbon dioxide. Will create a concentration gradient in ETC oxidative phosphorylation. Aerobic cellular includes three major stages glycolysis.
All of the above. In summary cellular respiration is the process of making energy from glucose and oxygen. Which of the following statements describe the role of oxygen in respiration.
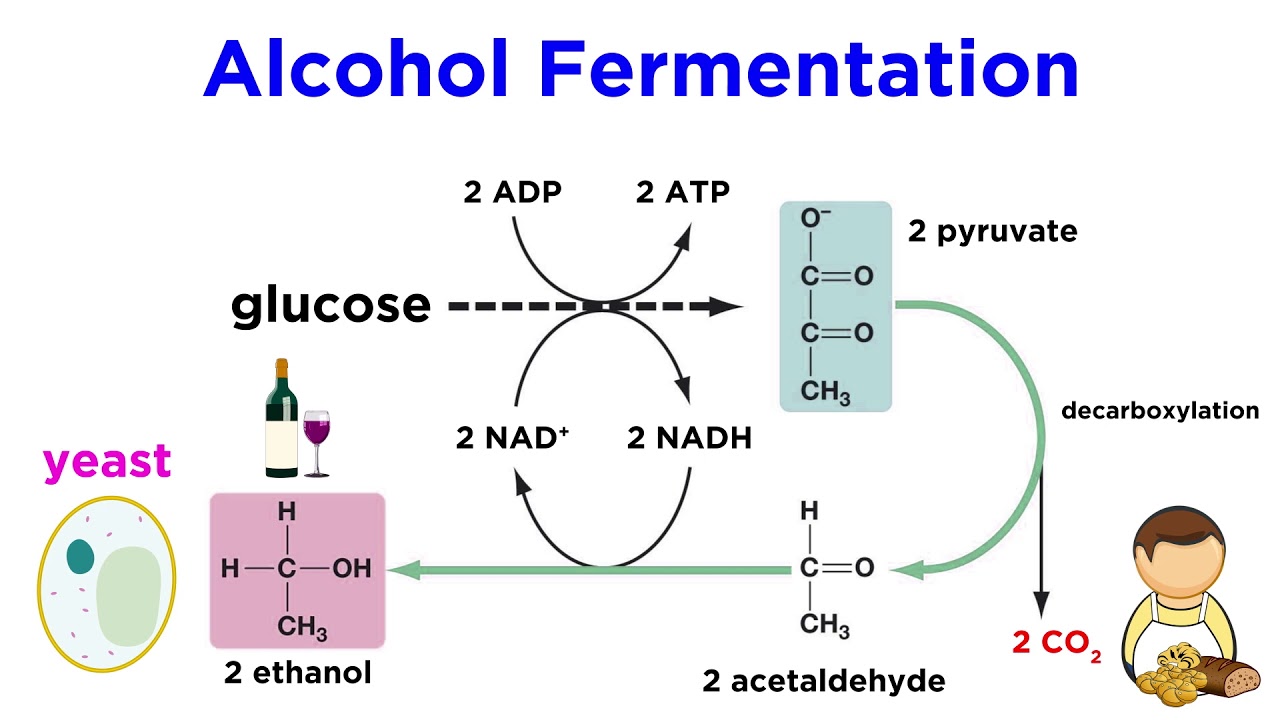
There are two types of cellular respiration aerobic and anaerobic. Aerobic cellular respiration is in direct contrast of anaerobic respiration which does not require oxygen. Which one of the following describes the process of aerobic cellular respiration.
Explain why ATP is. Aerobic Cellular Respiration is a part of the cellular respiration and it plays an important role in producing energy that is required for the various functions of the cell.
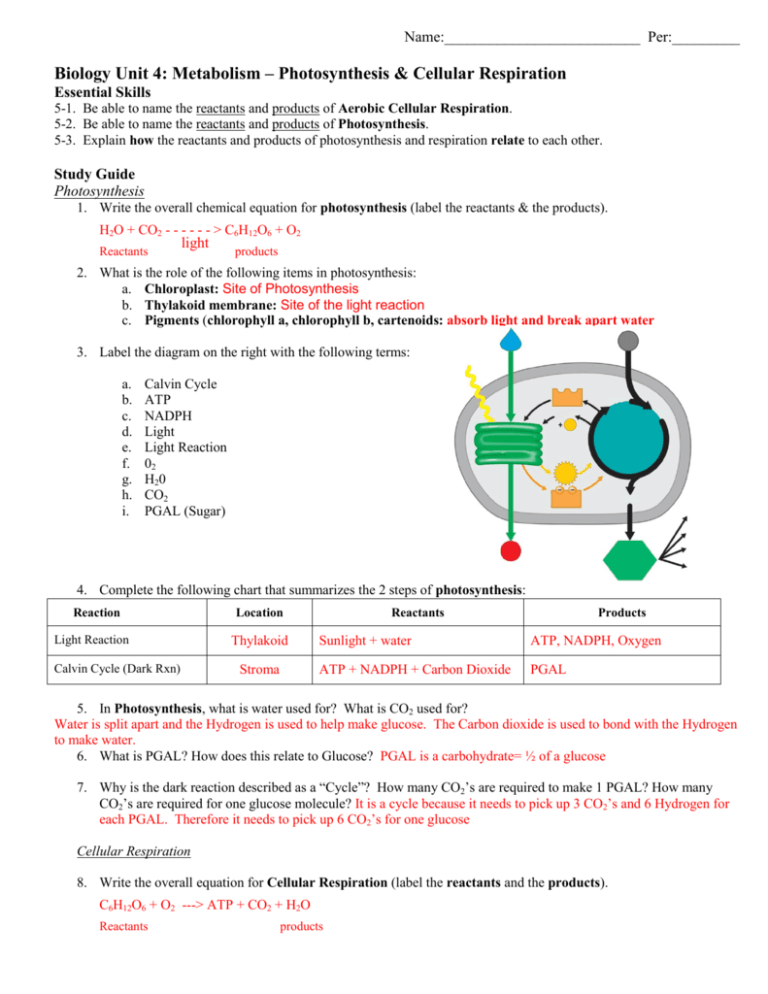
Biology Unit 4 Metabolism Photosynthesis Cellular

Cellular Respiration Review Article Khan Academy

Cellular Respiration Definition Equation Cycle Process Reactants Products Britannica
4 10 Cellular Respiration Human Biology
Anaerobic Respiration And Fermentation Youtube
Powering The Cell Cellular Respiration Ck 12 Foundation
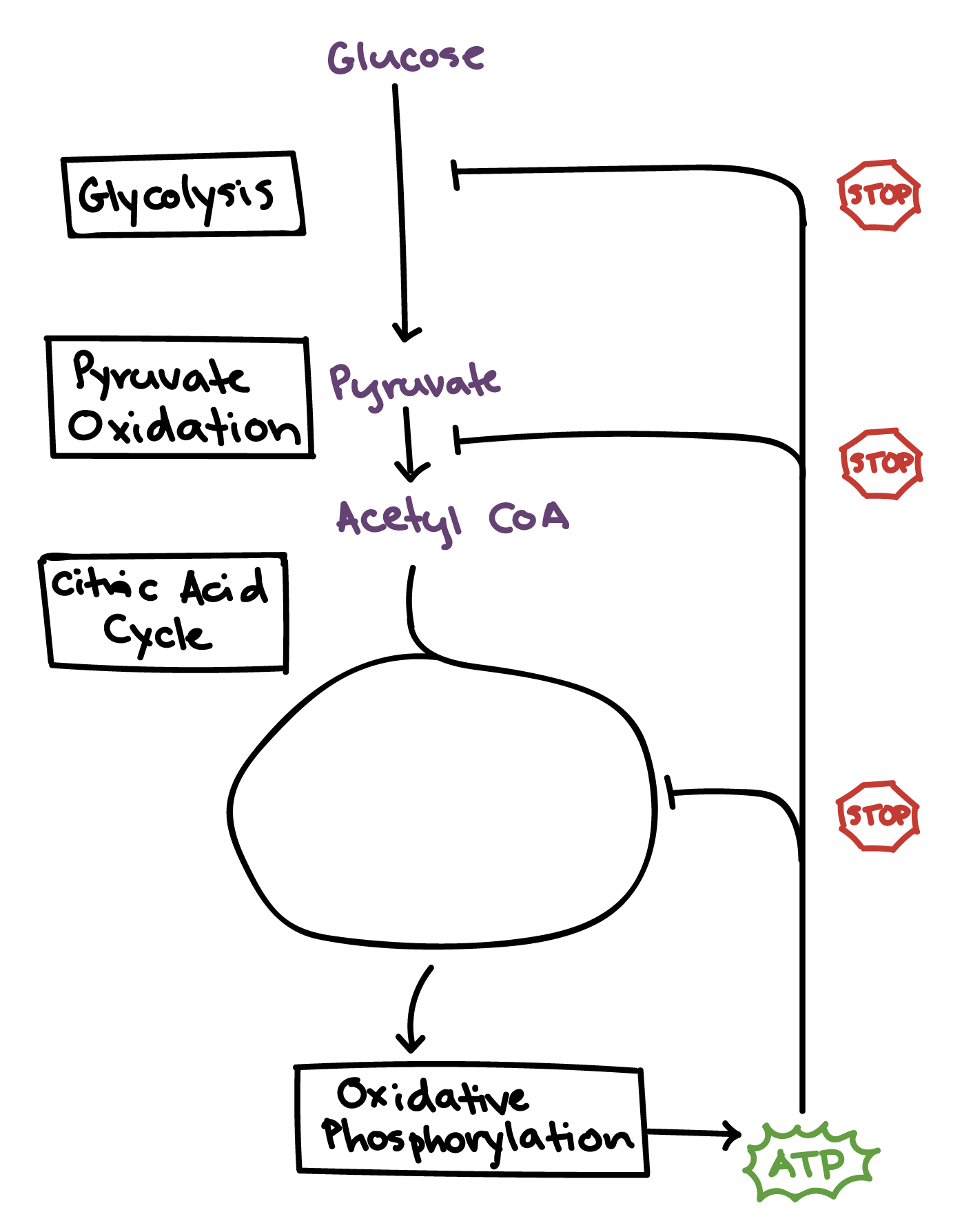
Regulation Of Cellular Respiration Article Khan Academy

Overview Of Cellular Respiration Human Physiology Openstax Cnx
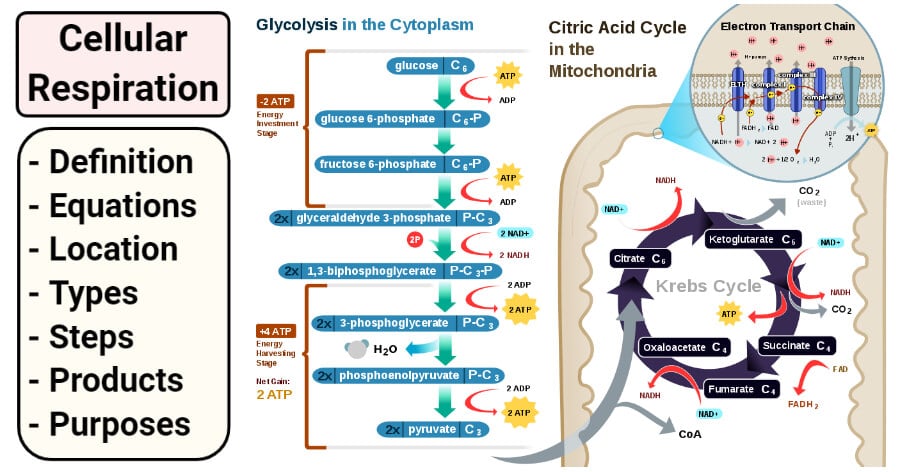
Cellular Respiration Definition Equations Types Steps Products

Cellular Respiration Ck 12 Foundation

Cellular Respiration Students Britannica Kids Homework Help
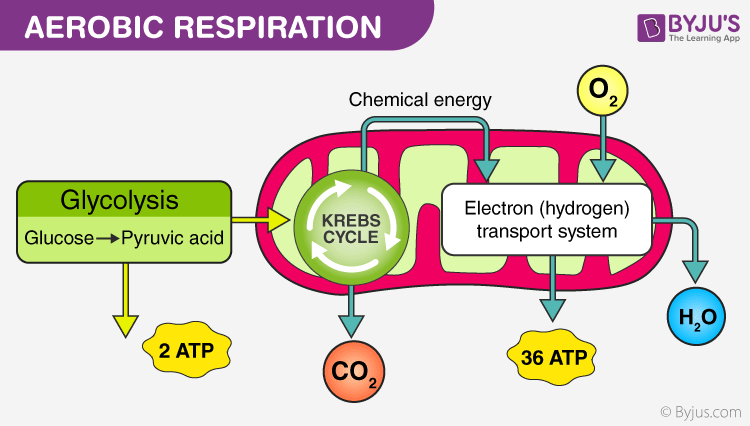
What Is Aerobic Respiration Definition Diagram And Steps

Origins Of Cell Compartmentalization Ap Biology Biology Dictionary
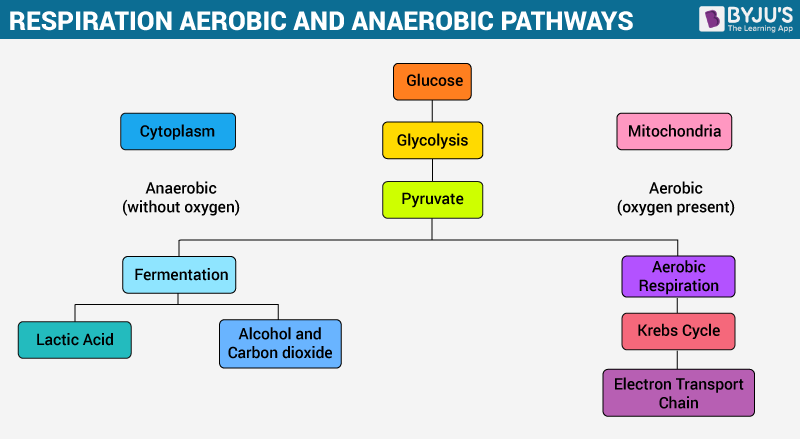
Overview Of Cellular Respiration Aerobic Anaerobic Respiration

Learn About Cellular Respiration And Mitochondria Chegg Com
Cell Respiration Wyzant Lessons

Cellular Respiration Definition Equation Cycle Process Reactants Products Britannica


Comments
Post a Comment